Definition – Chemical peeling is a medical procedure which includes application of a chemical agent to the skin, causing controlled destruction of the epidermis, with or without the dermis, leading to exfoliation and removal of superficial lesions, followed by regeneration of new epidermal and dermal tissues.
In simple words chemical peeling or chemical rejuvenation is procedure where a chemical agent or combination of agents of defined strength are applied the skin causing a controlled destruction of layers of the skin. This is followed by regeneration and remodeling leading to improvement of texture and surface abnormalities. It is a safe, effective and affordable option for improving skin ageing and imperfections.
Skin Histology
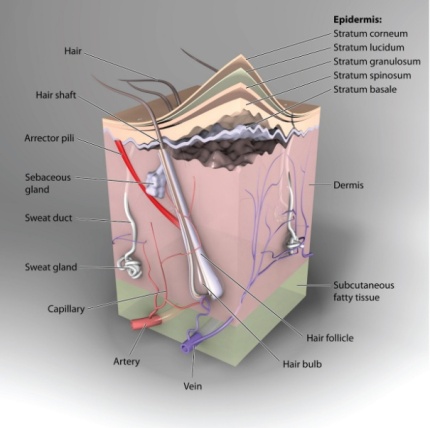
Skin is considered the largest organ of the body and has many different functions. The skin is divided in two main regions, the epidermis and the dermis. The dermis is attached to an underlying hypodermis also called subcutaneous connective tissue.
Epidermis – It is the most superficial layer of the skin. The first barrier of protection from the invasion of foreign substances. The epidermis is divided into four layers – stratum corneum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum and stratum basalis(basal layer).
Dermis – It is composed of fibroblasts which are responsible for secreting collagen, elastin and ground substance that gives support and elasticity to skin. It supplies the epidermis with nutrients and has its role in thermoregulation. The dermis is subdivided into two zones, upper papillary and lower reticular layer.
Classification of peels according to histological depth
Very superficial peel – Exfoliation of the stratum cormeum, without any epidermal necrosis.
Superficial peel – Destruction of the full epidermis, up to the basal layer
Medium peel – Destruction of the epidermis, papillary dermis and upto the upper one third of the reticular dermis.
Deep peel – Necrosis of the entire epidermis and papillary dermis with inflammation extending to the mid reticular dermis.
Classification of chemical peeling agents
Very superficial Peel:
Glycolic Acid 30-50% applied for 1-2 minutes
TCA* 10% applied as one coat
Jessner’s solution 1-3 coats
Superficial Peel:
Glycolic acid 50-70% applied for 2-10 mins (depending on the type and thickness of the skin)
TCA 10-30%
Jessner’s solution 4-10 coats
Very superficial and superficial Peels are the mildest form and often called, “the lunchtime peel.” These peels break down corneocyte adhesion, causing dead skin cells to shed off to reveal the fresh, healthy underlying skin. These peels address minor skin irregularities like discoloration, acne, surface scarring, fine lines, and sun spots.
Medium Peel:
Glycolic acid 70% applied for 3-30 mins (depending on the type and thickness of the skin)
TCA 35-50%
Glycolic Acid 70% plus TCA 35%
Jessner’s solution plus TCA 35%
Deep Peel:
Phenol 88%
Baker Gordon phenol formula
Medium and deep peels increase the collagen and glycosaminoglycans content, cause collagen remodeling and increase dermal thickness to improve the clinical appearance of the skin with reduced wrinkles, skin tightening and pigmentary dyschromia.
Reason behind chemical peeling:
Wound healing process is an important reason for rejuvenation. The phases of wound healing after chemical exfoliation are apparent:
• Inflammatory phase (1-5 days) – This phase is evident after peeling as erythma and swelling on the skin
• Proliferative phase (2-21 days) – In superficial peels, the basement membrane is intact, hence normal epidermis is restored in 2 to 3 days. In medium to deep peels, wound is below basement membrane and re-epithelialization takes time.
• Remodeling phase (3 weeks to 2 years) – collagen remodeling is the main reason that chemical peels cause rejuvenation and reduce wrinkles.
Indications for peels:
1. Pigmentary disorders
a. Resistant melasma
b. Pigmented cosmetic dermatitis
c. Freckles
d. Lentigines
e. Post inflammatory hyperpigmentation
2. Acne
a. Comedonal acne
b. Post acne scars
c. Acne cosmetic
d. Acne excoriee
3. Cosmetic
a. Photoageing
b. Fine wrinkling
c. Skin glow and rejuvenation
d. Oily to rough skin
e. Actinic keratosis
4. Miscellaneous
a. Keratosis pilaris
b. Macular amyloidosis
c. Dilated pores
d. Seborrheic keratoses
Contraindications:
• Active bacterial, viral and fungal infection and open wounds
• Oral isotretinoin use within the past three months
• Pregnancy and breast feeding
• History of keloid formation
• History of taking oral contraceptive and photosensitive drugs
• Unrealistic patient expectation
• Uncooperative patient, eg. Patient is careless about sun exposure or application of medicine
• For medium depth and deep peels, history of abnormal scarring, atrophic skin and isotretinoin use in the last six months.
How to choose a patient:
A patient should be chosen depending upon 4P’s:
P – Pathology
P – Point of depth required
P – Patients skin
P – Previous peeling agents
Newer peels:
Many peels like mandelic acid, kojic acid, lactic acid, citric acid and many more have been introduced in the market which are also available in combination. These peels are not only more skin friendly but also more patient friendly. They have buffering agents like licorice extract and willow bark extract to minimize irritation to skin and antioxidants to infuse the skin with restorative nutrients. The change in the skin often occurs at cellular level and are not apparent to the naked hence making it more popular amongst busy patients who are seeking effective treatments quickly with little or no downtime.
Benefits of chemical peels:

• The skin becomes noticeably smoother and rejuvenated.
• It reduces pigmentation, improves dull and uneven skin tone, reduces signs of photoagaeing, acne and enlarged pores.
• Removes dead and damaged skin cells and improves skin texture
• Helps in removal of tan
• Skin becomes brighter and more vivid because chemical peels not only cause re-epithelialization of the epidermis but also collagen remodeling.
Pre peel and post peel precautions:
• Patient has to be motivated enough to get multiple sittings of the peel ( 4-8, depending on the indication and type of peel) every 2-3 weekly to get the desired result.
• Patient should not wax, bleach, scrub, shave(the same day) or get any other aesthetic procedure like microdermabrasion, ipl, derma-roller one day before the chemical peel procedure. A gap of atleast 7 days before and after the peel should be maintained.
• Patient should use a mild soap/ non soap cleanser after the peel
• Broad spectrum sunscreen and moisturizer should be used liberally, atleast 2-3 times a day and sun exposure should be avoided.
• Patient should be strictly prohibited from scratching, picking or scrubbing the skin.
Take home message:
Chemical peeling is a simple office procedure for the treatment of acne, pigmentation, skin rejuvenation and photoageing. These are not one time procedures but require 6-8 sessions and maintenance peels to achieve maximum improvement and prevent recurrences. The newer peels are safer and effective.
Abbreviation used:
TCA – Trichloroacetic Acid
Thank you for providing the information. I am learning so much now.
ReplyDeleteWhat are the Benefits of Chemical Peels